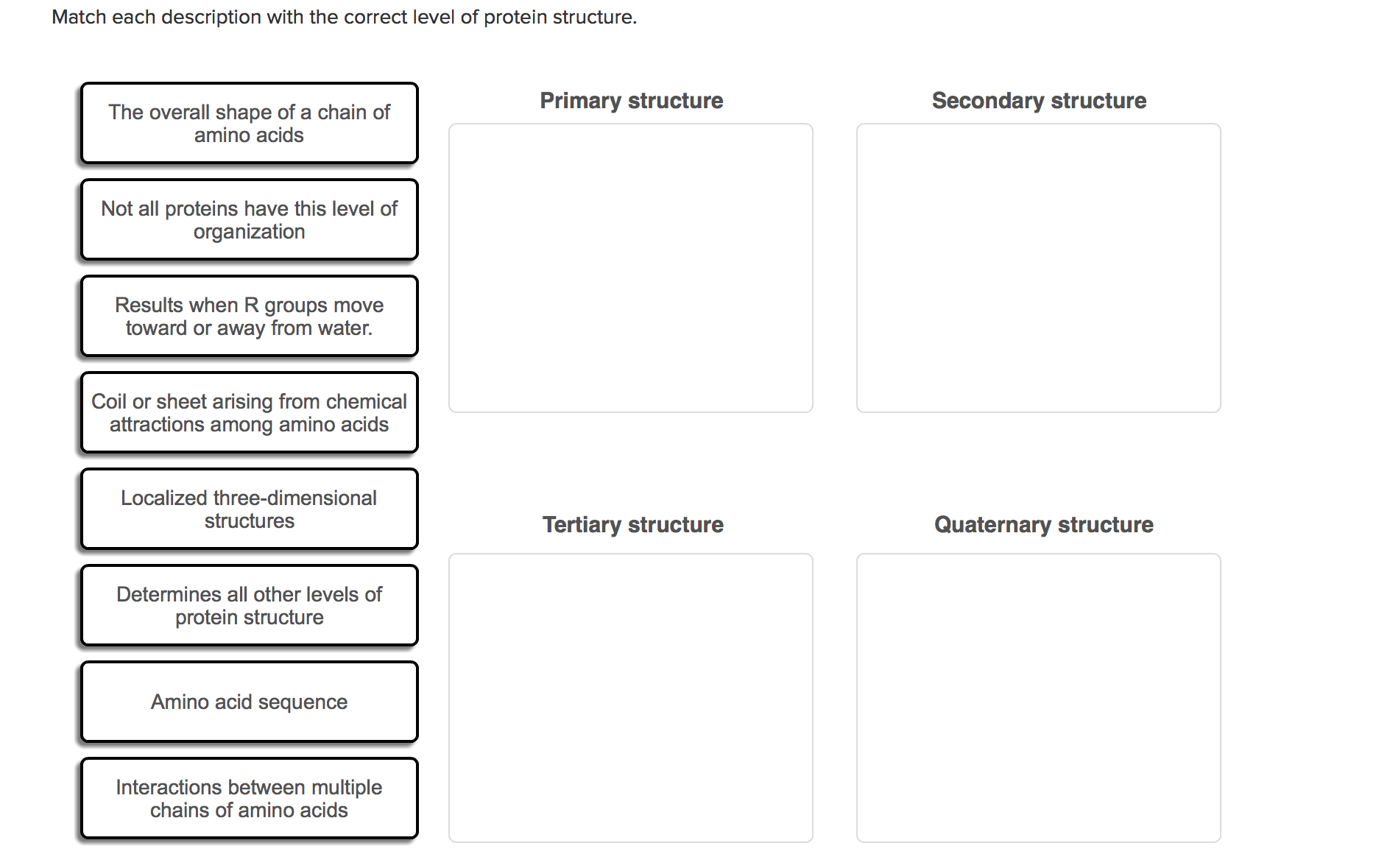
Identify the Level of Protein Structure Matching Each Description.
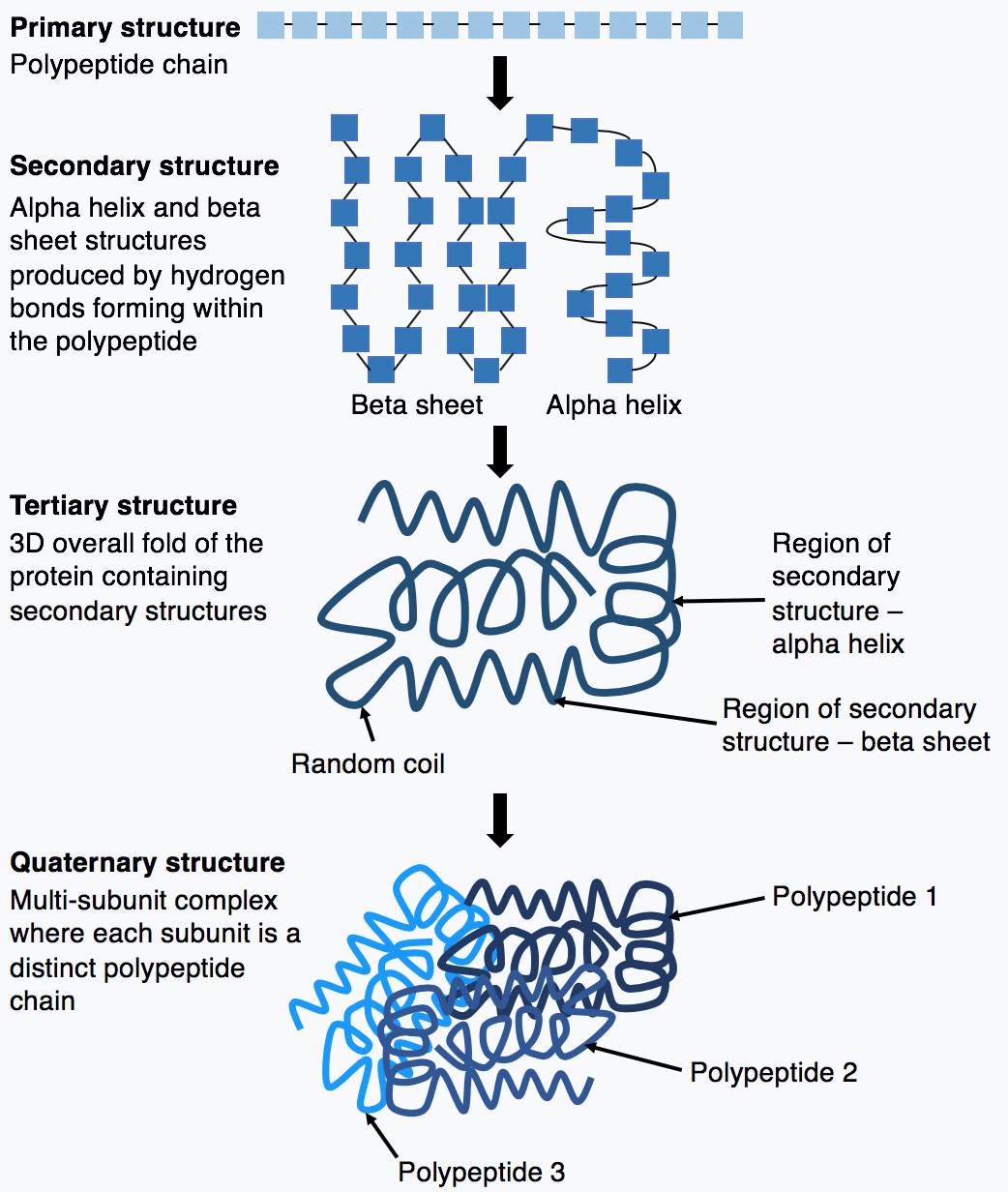
Secondary structure is the next level up from the primary structure and is the regular folding of regions into specific structural patterns within one polypeptide chain. Then choose the descriptions from the list below that go with each of the levels.

Levels Of Protein Organization
Chaperones are released as protein is transferred to a channel in the outer membrane.

. Match each description to its correct level of protein structure Polypeptides are made up of amino acids connected via peptide bonds the sequence of which is determined by genes. The Shape and Structure of Proteins. The primary structure of protein is the hierarchys basic level and is the particular linear sequence of amino acids comprising one polypeptide chain.
Nucleus Contains instructions for protein synthesis and cell reproduction. Small 3D features determined by hydrogen bonding Choose. For each characteristic identify if it is present in bacteria archaea or both.
Chaperones bind to protein as it enters the matrix. The formation of a protein is created using a hierarchy of structures. The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin.
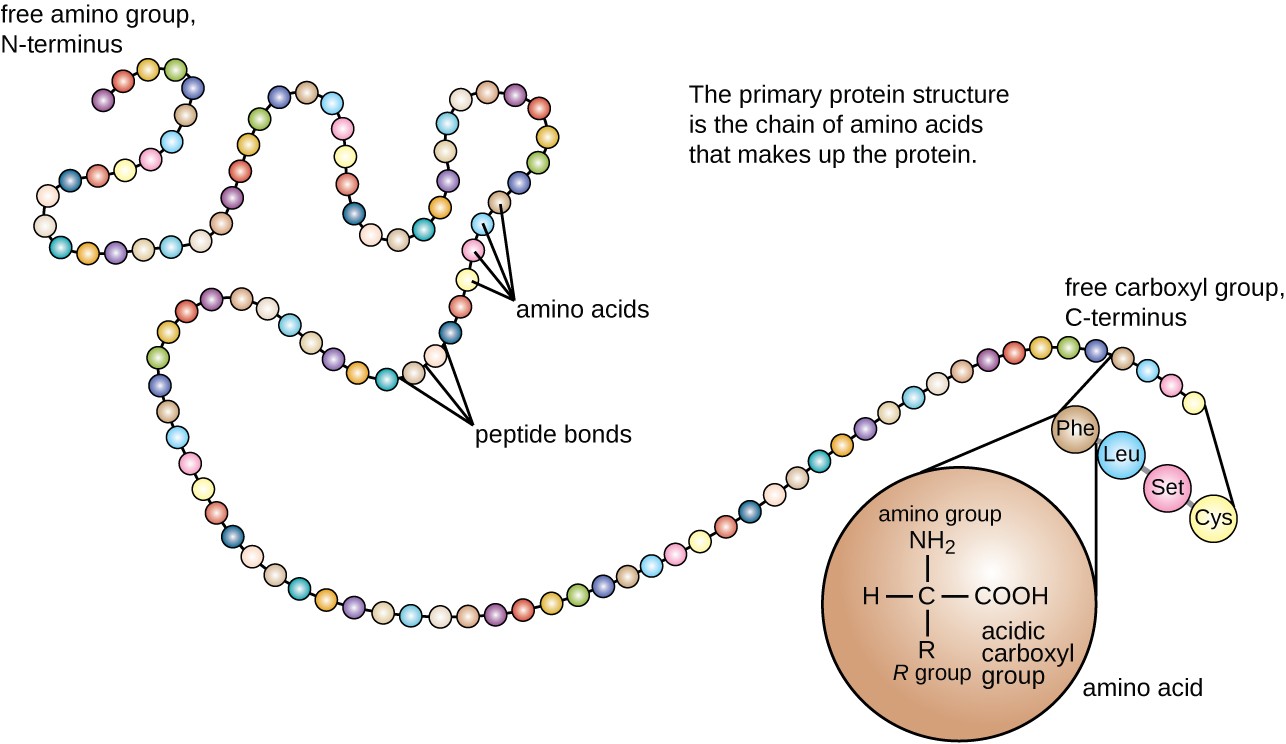
The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. Overall three-dimensional shape B. The different levels of protein structure are known as primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure.
The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. Primary structure the linear sequence of amino acids held together by covalent. Select all that apply.
Not yet answered Points possible. The exact order of the amino acids in a specific protein is the. Small 3D features determined by hydrogen bonding Choose.
Amino acid sequence C. Give the name and description of the first level of protein structure. And 1 mol of propane C_3H_8.
Sequence is DIFFERENT - How to determine the COMPOSITION. Not yet answered Points possible. - Contains Glycine at every 3rd residue.
By convention four levels of protein organization may be identified. From a chemical point of view proteins are by far the most structurally complex and functionally sophisticated molecules known. Identify the level of protein structure matching each description.
Tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional structure of an. They carry out a wide variety of organism functions including DNA replication transporting molecules catalyzing metabolic reactions and providing structural support to cells. Four levels of protein structure.
What levels of protein structure would be affected if all hydrogen bonding interactions were prevented. Primary structure Tertiary structure Secondary. The sequence of amino acids Choose Overall 3D shape of a protein Choose Interaction of.
No partial credit. Questions of BACK. Choose from these descriptions.
Martix-targeting sequence binds to receptor. The sequence of amino acids Choose. Match the organelle with its function 1.
Participates in lipid synthesis and synthesis of membrane or secreted proteins. Students should be able to identify the four levels of protein structure and the molecular forces or interactions responsible for stabilizing each level of structure. 100 Identify the level of protein structure matching each description.
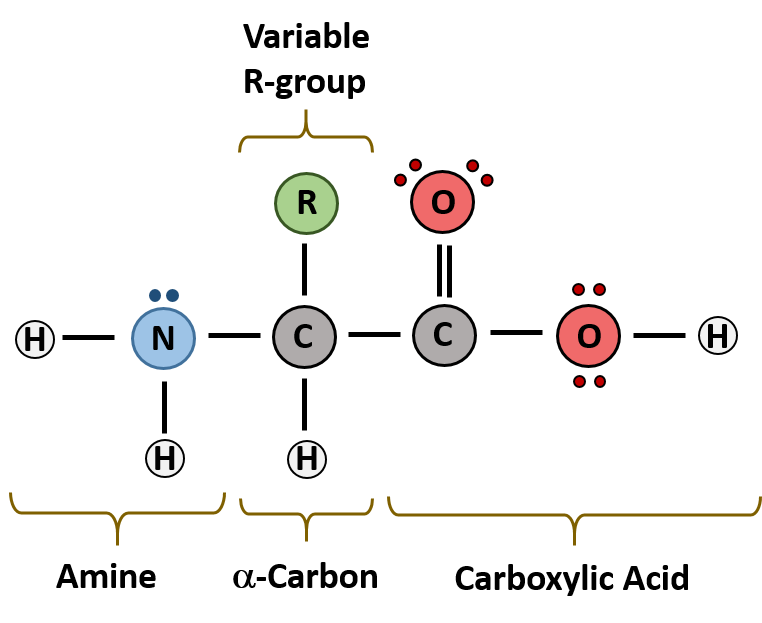
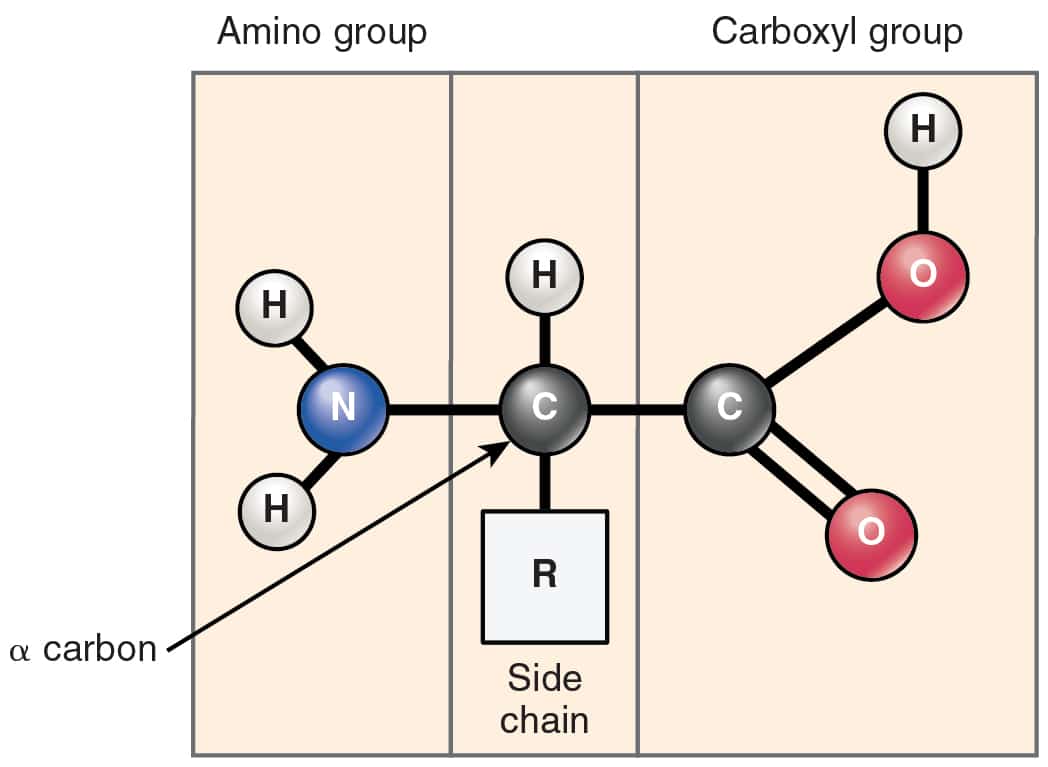
Proteins are polypeptide structures consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. M-L-D-G-C-G Peptide A. Matrix-targeting sequence binds to receptor.
2 There may be several answers for some of these. Chlorine sodium or carbon. Overall 3D shape of a protein Choose.
100 Identify the level of protein structure matching each description Small 3D features determined by hydrogen bonding. Overall 3D shape of a protein Tertiary structure Interaction of multiple of protein units Choose. Match each name with the appropriate structure in the diagram.
Match each description with the most appropriate atom of the choices given. Consists of the linear amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. This is perhaps not surprising once one realizes that the structure and chemistry of each protein has been developed and fine-tuned over billions of years of evolutionary history.
- Contains heptad repeats. The secondary structure consists of local packing of polypeptide chain into α-helices and β-sheets due to hydrogen bonds between peptide bond central carbon backbone. - Contains intrachain hydrogen bonds.
Endoplasmic reticulum Intracellular compartment forms transport vesicles. Identify each of the levels of protein structure in the diagrams. Levels of Protein Organization A 2014 Foundations of Medicine eLAB.
Match the protein to the descriptions. Primary Structure of Proteins The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain. Levels of Protein Organization.
Chaperone proteins keep proteins unfolded. -The level of organization that is more complex than an atom but less complex than an organelle is an molecule-Molecules may be assembled into a microscopic structure called an organelle which carries out specific functions within a cell-The simplest level of organization that can carry out all of the functions of life is an cell. Levels of Protein Structure.
A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types. Proteins have four levels of organization.
1 The protein to consider here is collagen. Calculate the enthalpy change for each reaction to determine the amount of energy as heat evolved by. Secondary structure is the local spatial arrangement of a polypeptides backbone main chain atoms.
PRIMARY STRUCTURE 1 - Defined non-random sequence of amino acids along the peptide backbone o Described in two ways. Biologists distinguish 4 levels of protein structure. Primary structure refers to the linear sequence of the amino acids connected by the peptide bonds.
20 different amino acids are found in proteins. M-L-C-D-G-G Peptide B. For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below.
These are called the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structures of the protein. Protein is transferred to a channel in the inner membrane 5. A proteins primary structure is defined as the amino acid sequence of its polypeptide chain.
The sequence of amino acids Choose. Check all that apply.
Protein Structure Amino Acids Primary Teachmephysiology

Levels Of Organization In Living Things Sort Atom To Organism Biology Classroom Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry
How Are Protein Molecules Structured Quora

Major Differences Com Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Protein Biology
Match Each Description With The Correct Level Of Protein Structure At Level

Chapter 3 Protein Structure And Function Flashcards Quizlet

Solved Match The Level Of Protein Structure With The Correct Chegg Com

Levels Of Protein Organization
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Solved Match Each Description With The Correct Level Of Chegg Com
Protein Structure Amino Acids Primary Teachmephysiology

Compound Interest Chemistry Science Activities For Kids Chemical Structure

Levels Of Protein Organization

Secondary Structure Of Proteins A Stick Ribbon Stick With Line Side Download Scientific Diagram

Match Each Description With The Correct Level Of Protein Structure At Level
Match Each Description With The Correct Level Of Protein Structure At Level


Comments
Post a Comment